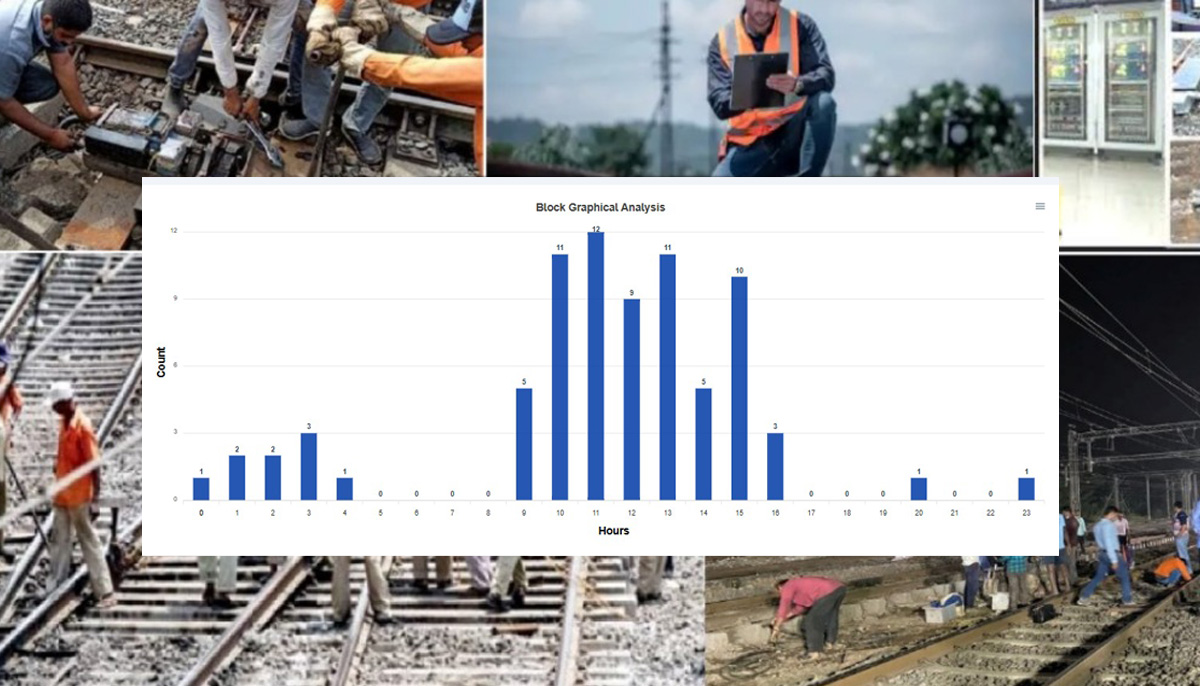
The Rolling Block Management System (RBMS) is an advanced system designed to manage train movements and track maintenance in a more dynamic and efficient way compared to traditional fixed block signaling systems. It is primarily used to enhance operational safety, optimize track utilization, and ensure uninterrupted train services while enabling scheduled maintenance activities
Enhanced Safety
- Real-time Monitoring: Tracks train positions dynamically to prevent collisions and minimize risks during block operations.
- Automated Alerts: Warns of potential signal violations or unsafe conditions, reducing human error.
Improved Operational Efficiency
- Reduced Downtime: Rolling blocks allow for selective track maintenance without completely halting operations, ensuring minimal disruption.
- Dynamic Scheduling: Facilitates flexible train scheduling, accommodating freight and passenger traffic seamlessly.
Optimal Utilization of Resources
- Better Crew Management: Efficiently assigns and monitors workforce availability for track maintenance and signaling operations.
Cost Savings
- Fuel Efficiency: Optimized train movement reduces idle time and unnecessary acceleration, leading to lower fuel consumption.
- Reduced Wear and Tear: Improved scheduling and fewer abrupt halts contribute to longer lifespan for tracks and rolling stock.
Real-Time Data Integration
- Centralized Control: Integrates with the Indian Railways Operations Management System (IROMS) to provide live data for better decision-making.
- Data Analytics: Enables predictive analytics for future maintenance and operational planning.
Increased Line Capacity
- Efficient Track Usage: Rolling blocks maximize track availability, allowing for more trains to operate without compromising safety.
- Reduced Congestion: Minimizes bottlenecks in high-traffic zones, ensuring smoother flow.
Eco-Friendly Operations
Lower Emissions: Streamlined operations contribute to reduced carbon emissions, supporting sustainability goals.
Key Features of the Rolling Block Management System
- Dynamic Block Operations
- Unlike traditional fixed blocks, where trains operate within predefined sections, RBMS uses a moving block system to dynamically allocate track segments based on real-time train positions.
- Real-Time Train Tracking
- Employs technologies like GPS, radio communication, and sensors to monitor train locations in real time.
- Tracks train speed, direction, and proximity to other trains.
- Integrated Maintenance Management
- Allows selective track maintenance (rolling blocks) without halting all train operations in a particular section.
- Maintenance activities are coordinated to ensure minimal disruption to train schedules.
- Centralized Control System
- Combines inputs from signaling systems, train monitoring systems, and track condition monitoring tools to provide a unified platform for decision-making.
- Works seamlessly with advanced train control systems like CBTC (Communications-Based Train Control) or ETCS (European Train Control System).
- Predictive Analytics
- Utilizes historical data and real-time monitoring to predict maintenance needs, track wear, and potential faults.
- Ensures proactive planning and resource allocation.
Applications of Rolling Block Management System in Indian Railways
- Track Maintenance Without Halting Traffic
- Enables rolling blocks where maintenance is carried out in a specific section while trains operate on adjacent tracks.
- Freight Corridor Optimization
- Essential for handling high traffic in dedicated freight corridors by managing dynamic train operations efficiently.
- Suburban and High-Density Rail Networks
- Useful in metro and suburban systems where high train frequency requires better track utilization.
- Integration with Indian Railways Operations Management System (IROMS)
- Provides data to IROMS for centralized train scheduling and real-time decision-making.
How RBMS Differs from Traditional Systems
| Aspect | Traditional Fixed Blocks | Rolling Block System |
| Block Allocation | Predefined, fixed-length blocks | Dynamic, based on train position |
| Safety Margins | Larger, fixed safety distances | Optimized, real-time adjustments |
| Maintenance Impact | Entire block needs closure | Specific track section closed |
| Technology Integration | Limited | High (GPS, IoT, AI, etc.) |