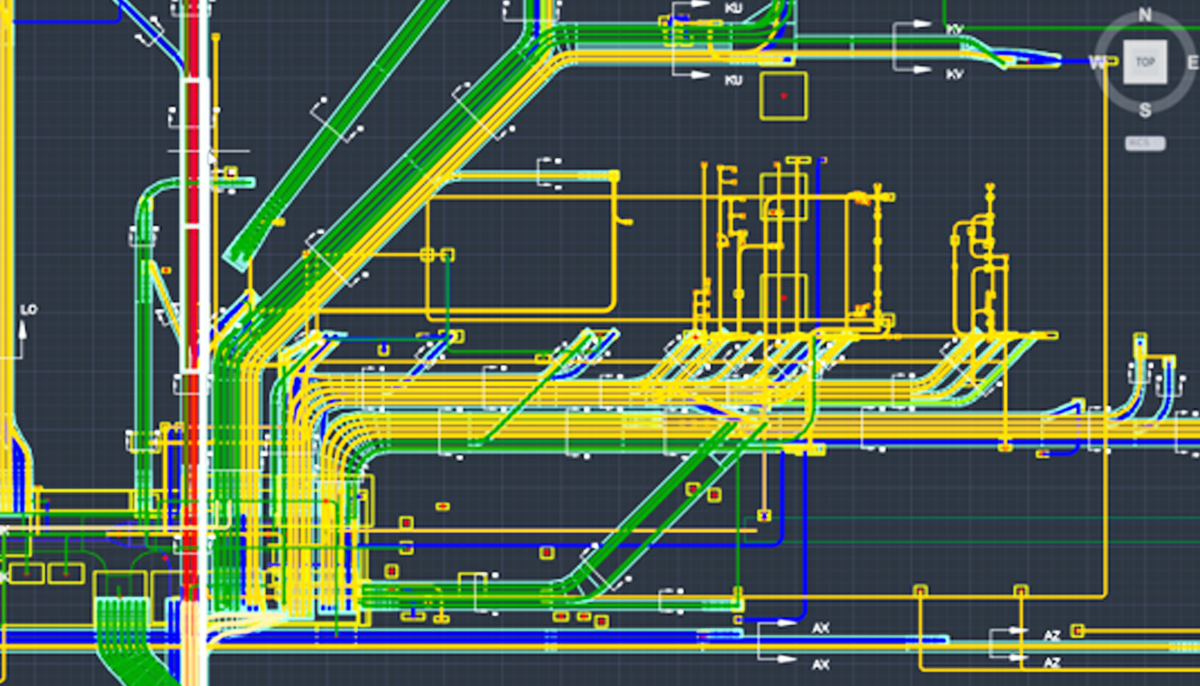
The Cable Management System (CMS) in Indian Railways is a structured approach to organize, protect, and maintain the network of cables that support critical railway operations, including signaling, telecommunication, electrical systems, and data transmission. It is essential for ensuring uninterrupted railway operations, safety, and efficient maintenance.
Types of Cables Used in Indian Railways
- Signalling Cables
- Multi-core cables for interlocking and track circuiting.
- Telecommunication Cables
- Optical fiber cables for communication networks.
- Copper cables for voice and data transmission.
- Power Cables
- High-voltage cables for traction systems and electrical supply.
- Low-voltage cables for station and signal equipment.
- Data Cables
- Ethernet cables for networking.
- Specialized cables for train control and management systems.
Key Components of Cable Management in Indian Railways
- Cable Laying and Routing
- Cables are laid systematically along tracks or underground through trenches or ducts.
- Precise routing plans are implemented to prevent cable damage and interference between different systems.
- Cable Protection Systems
- Use of PVC conduits, HDPE pipes, or concrete troughs to shield cables from environmental factors like moisture, rodents, and physical damage.
- Trenches and underground installations for additional protection.
- Identification and Labelling
- Proper labelling of cables to differentiate between signalling, telecommunication, and electrical lines.
- Use of cable markers at regular intervals for easy identification during maintenance.
- Cable Termination and Jointing
- High-quality jointing kits and termination boxes ensure secure and durable connections.
- Use of advanced technologies such as heat-shrinkable joints and plug-and-play connectors for ease of installation.
- Signal Interference Management
- Shielding and earthing mechanisms to prevent electromagnetic interference between cables.
- Compliance with standards to ensure reliable signal transmission.
- Monitoring and Maintenance
- Periodic inspections to detect wear and tear, overheating, or voltage fluctuations.
- Integration with digital tools for real-time monitoring of cable conditions.
- Emergency Preparedness
- Stockpiling spare cables and tools for quick restoration in case of damage.
- Rapid response teams for cable-related emergencies.
Importance of Cable Management System
- Operational Safety
- Prevents accidental short circuits, power failures, and signal disruptions.
- Reduces the risk of hazards caused by exposed or damaged cables.
- Reliability
- Ensures uninterrupted operations by safeguarding critical signaling and telecommunication systems.
- Ease of Maintenance
- Organized and labeled cables simplify troubleshooting and reduce downtime during repairs.
- Durability and Longevity
- Proper protection increases the lifespan of cables, minimizing replacement costs.
- Aesthetic and Environmental Compliance
- Properly laid cables maintain trackside cleanliness and align with eco-friendly initiatives.
Mediazation Cable Management for Indian Railways
- Digital Cable Monitoring
- Use of IoT sensors for real-time monitoring of cable performance and fault detection.
- Fiber Optic Expansion
- Deployment of optical fiber cables for high-speed data transmission and future-proofing communication systems.
- Modular Cable Ducts
- Introduction of pre-fabricated, modular cable ducts for quick installation and better protection.
- Cable Management Software
Tools for tracking cable layouts, planning new installations, and managing maintenance schedules.
Challenges in Cable Management
- Digital Cable Monitoring
- Use of IoT sensors for real-time monitoring of cable performance and fault detection.
- Fiber Optic Expansion
- Deployment of optical fiber cables for high-speed data transmission and future-proofing communication systems.
- Modular Cable Ducts
- Introduction of pre-fabricated, modular cable ducts for quick installation and better protection.
- Cable Management Software
Tools for tracking cable layouts, planning new installations, and managing maintenance schedules.
- Vandalism and Theft
- Protection measures like anti-theft covers and enhanced surveillance are required.
- Environmental Hazards
- Floods, landslides, and extreme weather can damage cable infrastructure.
- Aging Infrastructure
Upgrading older cable systems to modern standards is a continuous process.
Significance for Indian Railways
Effective cable management is critical for modernizing Indian Railways, enabling seamless signaling, communication, and electrical systems. It supports the Digital India Initiative and facilitates integration with advanced systems like the Indian Railways Operations Management System (IROMS), enhancing safety, efficiency, and reliability.